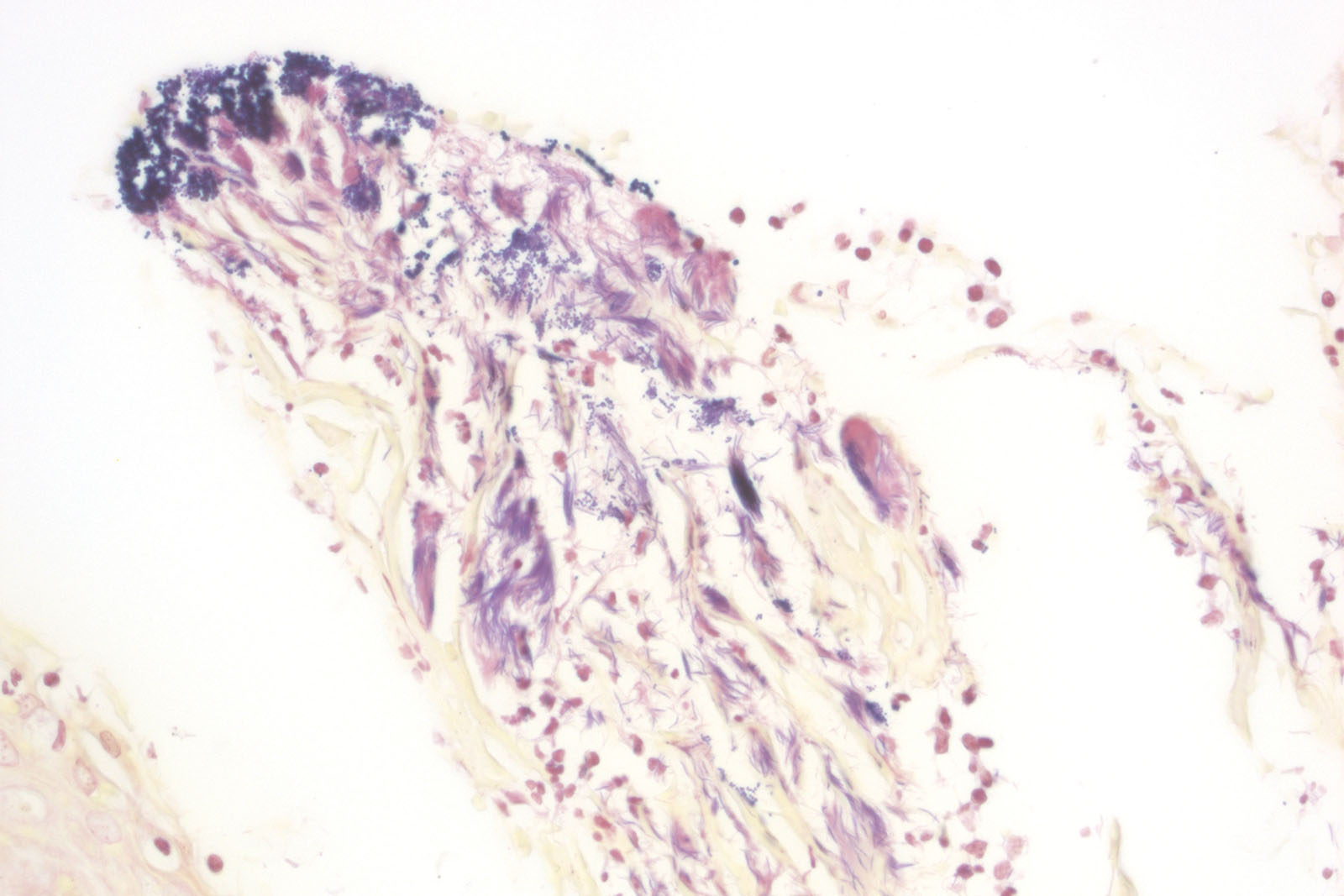
Introduction
Gram staining is a method of differentiating bacterial species and it is commonly known and used in microbiology. It is also one of the most frequently used diagnostic methods in hospital and clinical laboratories. Gram staining differentiates bacteria into two groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. That division is based on the two groups’ bacterial membrane structural differences, i.e. their capability of retaining the dye. Gram-positive bacteria have a thicker cellular membrane which enables retaining the dye inside the cell by treating them with iodine solution that creates insoluble iodine and primary dye complex. Gram-negative bacteria have thinner cellular membrane structure which cannot retain the dye. It washes away through the membrane, and using counterstaining forms the basis for differentiating between the two bacteria groups. BioGnost’s BioGram Histo kit contains Gram Crystal Violet 1% solution, stabilized Gram Lugol solution, two packages of Gram Decolorizer 2 solution, Gram Safranin solution and two packages of picric acid in acetone. Its characteristics make it an optimal bacteria staining agent which provides consistent results.